Air pollution is a serious issue that affects both the environment and human health. It consists of harmful substances released into the air, which can stem from various sources such as vehicles, factories, and even natural events like wildfires.
The science behind air pollution involves understanding the types of pollutants, how they disperse in the atmosphere, and their impact on climate and health.
When pollutants enter the air, they can lead to numerous health problems, including respiratory issues and cardiovascular diseases. In addition to its direct impacts on individuals, air pollution can also contribute to broader climate changes, affecting weather patterns and ecosystems.
Clean air is essential for healthy living, and knowing the science behind air pollution can empower communities to take action.
Understanding air pollution is crucial not only for personal health but also for the future of our planet. As more people become aware of its effects, the collective effort to reduce pollution and promote clean air becomes more attainable.
By exploring the science behind air pollution, readers can learn about the causes and solutions that contribute to a healthier environment.
Understanding Air Pollution and Its Sources

Air pollution consists of various harmful substances in the atmosphere. Understanding its components and origins is crucial for tackling this pressing issue.
The main contributors to air pollution include various gases and particulate matter released from both natural and human-made activities.
Composition of Air Pollutants
Air pollutants are made up of a mix of solids, liquids, and gases that can harm health and the environment. Key pollutants include:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas that results from incomplete fossil fuel combustion. It can cause health issues, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): These gases form when fossil fuels are burned at high temperatures. They play a significant role in smog and respiratory problems.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Produced mainly from coal burning and industrial processes, it can lead to acid rain and respiratory issues.
- Particulate Matter (PM): Tiny particles that penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, affecting heart and lung health.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Emitted from various solvents, paints, and fuels, they can contribute to smog and health problems.
Major Sources of Air Pollution
Air pollutants originate from various sources, each playing a distinct role in environmental degradation. Major sources include:
- Industrial Processes: Factories often release large amounts of CO, NOx, and sulfur dioxide during manufacturing.
- Vehicle Emissions: Cars and trucks are significant contributors of NOx and volatile organic compounds, especially in urban areas.
- Wildfires: Natural events like wildfires release a mix of carbon monoxide, particulate matter, and other pollutants into the air.
- Coal Burning: Power plants using coal are major sources of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, significantly impacting air quality.
Urbanization has also intensified pollution levels. As cities grow, traffic and construction increase, leading to higher emissions.
The Role of Human Activities
Human activities are a major driver of air pollution. Fossil fuel combustion for energy and transportation leads to significant emissions of harmful pollutants.
- Urban Growth: Increased urbanization results in more vehicles and industrial activities. This contributes to higher levels of NOx and CO.
- Agricultural Practices: Fertilizers and pesticides release VOCs into the atmosphere, which can contribute to air quality issues.
- Waste Management: Landfills emit methane, while burning waste releases pollutants like sulfur dioxide.
The impacts of air pollution extend beyond environmental concerns; they also affect public health and worker productivity, leading to long-term challenges related to climate change.
Health and Environmental Consequences of Air Pollution
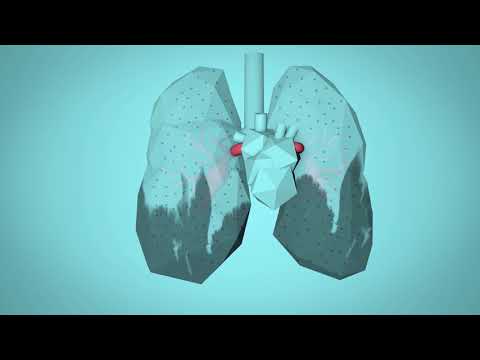
Air pollution has serious effects on both human health and the natural environment. Pollutants like particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide pose significant risks, leading to various health issues.
Additionally, air pollution contributes to climate change and can harm ecosystems through mechanisms like acid rain.
Impact on Human Health
Exposure to air pollution is linked to numerous health problems. Fine particles in the air can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing breathing difficulties and conditions like asthma.
Studies show that individuals with pre-existing health issues, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema, are especially vulnerable.
Moreover, long-term exposure can increase the risk of more severe diseases, including lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. According to research, high levels of particulate matter can lead to premature deaths.
Ground-level ozone, a primary component of smog, can worsen respiratory conditions and exacerbate symptoms in sensitive populations. By understanding these health impacts, preventive measures can be taken to reduce exposure.
Effects on Environment and Climate
Air pollution also has detrimental effects on the environment. It contributes to acid rain, which can harm plants and aquatic ecosystems by altering pH levels in soil and water bodies.
This can disrupt the balance of local ecosystems, affecting wildlife and plant growth.
Additionally, pollutants can drive climate change by releasing greenhouse gases. This not only impacts global temperatures but also leads to extreme weather events.
For example, higher ozone levels can significantly influence climate patterns, leading to fluctuations in weather. Understanding how air pollution affects both the environment and climate is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies, especially as urban areas expand and air quality worsens.
