The impact of global warming on the jet stream is a pressing concern for climate scientists. Recent studies indicate that changes in the temperature differential between the Arctic and the mid-latitudes are leading to a weaker, more wavy jet stream.
This weakened jet stream can result in more extreme weather patterns in the Northern Hemisphere, making events like heatwaves and heavy rainfall more frequent.
As the planet continues to warm, the dynamics of the jet stream alter significantly. Warmer temperatures in the Arctic can lead to a reduced pressure difference, causing the jet stream to become less stable. This shift not only affects weather forecasting but also poses risks to ecosystems and human activities.
Understanding how global warming weakens the jet stream is vital for grasping the broader implications of climate change. By following the latest climate science, readers can stay informed about how these atmospheric shifts impact daily life and the environment.
The Dynamics of the Jet Stream

Understanding the dynamics of the jet stream is crucial to grasping its impact on weather patterns and climate. Key elements include the concept of jet streams, the factors that influence their patterns, and their significant role in shaping weather events.
What is the Jet Stream?
The jet stream is a fast-moving current of air located in the upper atmosphere. It flows from west to east and plays a key role in the movement of weather systems.
There are two main types of jet streams: the polar jet stream, which forms at the boundary between cold polar air and warmer air to the south, and the subtropical jet stream, located further south. These narrow bands of wind are usually found at altitudes between 20,000 and 50,000 feet.
The position and strength of the jet stream are influenced by temperature differences between regions. As arctic warming occurs, these temperature contrasts can change, affecting the stability and flow of the jet stream. A stronger temperature contrast typically results in a more vigorous jet stream.
Factors Influencing Jet Stream Patterns
Several factors affect the patterns and behavior of jet streams. One major element is density contrast between air masses. Warm air is less dense than cold air, and when these two meet, they create instability, which can lead to stronger winds.
Additionally, the stratospheric polar vortex can play a critical role in influencing the polar jet stream, especially during winter months.
Changes in temperature patterns due to climate change are causing the jet stream to shift poleward. This shift affects weather systems around the globe and may lead to more extreme weather conditions, such as prolonged heat waves or colder winters.
Jet Streams and Weather Systems
Jet streams have a profound impact on weather systems. They act as a guide for the movement of storms and influence precipitation patterns.
For instance, when a jet stream dips southward, it can draw colder air down from the north while pushing warmer air upwards, leading to significant weather changes.
This process can create conditions for severe weather, including thunderstorms and heavy rainfall. Furthermore, the concept of quasi-resonant amplification explains how certain atmospheric waves can become reinforced along the jet stream, potentially prolonging weather events.
Meteorologists use models that take these jet stream behaviors into account for accurate weather forecasting.
Consequences of a Weakening Jet Stream
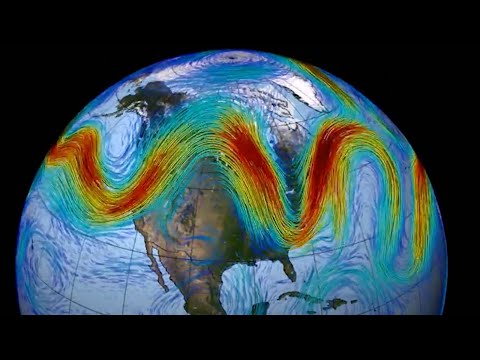
A weakening jet stream can lead to significant changes in global weather patterns. These changes can cause more frequent and intense weather events, impact regional climates, and have various socioeconomic effects.
Impact on Global Weather Events
The jet stream plays a crucial role in guiding weather systems around the globe. When it weakens, weather patterns become less stable, leading to extreme weather events.
For example, longer heat waves can occur as high-pressure systems stall over regions. Floods and droughts can also increase as the jet stream contributes to moisture distribution.
A slow moving jet stream can lead to persistent storms, resulting in increased rainfall and flooding in some areas, while creating dry conditions elsewhere.
These shifts affect mid-latitude weather by altering temperature contrasts, further intensifying storms and allowing for prolonged extreme weather conditions.
The Role of Arctic Amplification
Arctic amplification is a key factor in understanding the jet stream’s behavior. As the Arctic warms faster than other regions, it leads to sea ice loss.
This loss affects the temperature difference between the Arctic and mid-latitudes. As the temperature contrast weakens, the jet stream can slow down and become wavier.
This results in more extreme weather events, such as persistent droughts or heavy snowfall. A weakened jet stream can push cold air southward or block warm air, contributing to erratic weather patterns that can affect agriculture and water supplies.
Socioeconomic Ramifications of Changing Weather Patterns
A changing jet stream impacts not just the environment but also economies and societies.
Extreme weather events increase the costs associated with disaster relief and infrastructure repairs. For example, regions may face financial burdens from both floods and wildfires as conditions become less predictable.
The agriculture sector faces challenges too. Shifts in weather patterns affect crop yields and water availability, leading to food shortages or increased prices.
Communities dependent on stable weather conditions may struggle with adaptation, leading to displacement and increased pressure on social services.
These weather extremes, tied to the weakening jet stream, highlight the need for informed climate models and strategies to mitigate impact on livelihoods and ecosystems.
