The polar vortex is a strong band of winds that circles the Arctic and helps to keep cold air in its place. When the polar vortex spins backwards, it can lead to a significant disturbance in weather patterns, allowing colder air to escape into lower latitudes.
This unusual event often occurs due to sudden stratospheric warming, which can weaken the vortex and cause a reversal in wind direction.
Climate scientists closely monitor these changes because a backward-spinning polar vortex can bring extreme weather to regions that usually experience milder conditions. For instance, areas that typically enjoy warmer temperatures may face unexpected cold snaps, heavy snowfall, or even hail storms. This phenomenon is not just an interesting atmospheric occurrence; it can have real impacts on daily life and ecosystems.
As meteorological experts analyze this complex system, it becomes clear how interconnected weather patterns are across the globe. Understanding the implications of a vortex reversal helps in predicting potential shifts in climate and extreme weather events, emphasizing the importance of thorough research in atmospheric phenomena.
The Polar Vortex and its Typical Behavior
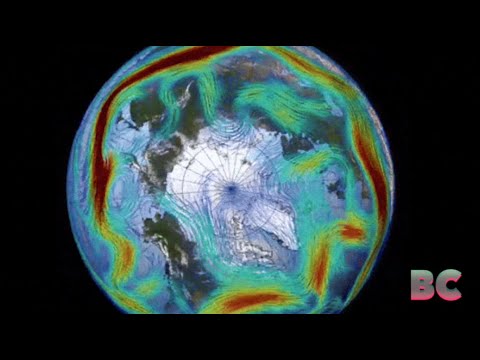
The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding the Earth’s poles. It plays a key role in weather patterns and can shift dramatically, influencing temperatures and storm systems across the globe.
The following subsections provide detailed insights into its structure, the Arctic region’s climatology, and the effects of stratospheric warming events.
Understanding the Polar Vortex Structure
The polar vortex is formed by strong winds that circulate around the Arctic region. These winds can reach speeds of over 250 km/h (155 mph) and create a stable, circular area of cold air.
The structure is typically strongest during the winter months, when the temperature difference between the poles and the equator is greatest.
As the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) monitors these winds, they have noted how shifts in the vortex can lead to changes in the jet stream. When the polar vortex is stable, the jet stream flows in a smooth path. However, when it weakens or shifts, it can cause the jet stream to become erratic, leading to unusual weather events across North America and Europe.
Climatology of the Arctic Region
The Arctic region’s climate is characterized by extreme cold and significant seasonal changes. During winter, temperatures can plunge well below freezing. This cold air forms the polar vortex, but climate change is altering its behavior.
Some climate scientists argue that rising global temperatures can make the polar vortex weaker and less stable.
With this instability, cold Arctic air can push southward, affecting lower latitudes where winter weather becomes severe. The interactions between atmospheric planetary waves and the polar vortex are crucial in understanding these shifts.
As a result, winters have become more challenging in many areas, resulting in increased snowfall and dangerously low temperatures.
Weather Impact of the Polar Vortex
The polar vortex significantly influences weather patterns across several regions. When it behaves normally, it contains cold air within the Arctic. However, during periods when it weakens, frigid air can move towards the equator. This change increases the likelihood of extreme weather events, such as heavy snowfall and bitterly cold temperatures.
These occurrences often coincide with severe winter storms affecting the Midwest and Northeast regions of the United States. As a result, many areas are experiencing disruptive weather due to the shifting polar vortex. Cold air outbreaks can also strain local infrastructure and resources as communities prepare for unexpected, harsh conditions.
Stratospheric Warming Events
Stratospheric warming events occur when temperatures in the stratosphere rise rapidly. These events can lead to a reversal of the polar vortex, causing it to spin backwards. When this happens, cold air typically trapped in the Arctic can spill down into lower latitudes.
Such warming can disrupt normal weather patterns, resulting in extreme cold spells or unusual warmth in different regions. Monitoring these phenomena is vital for forecasting and preparing for the impacts on weather conditions. Understanding these dynamics allows meteorologists to predict and inform the public about potential hazards linked to the polar vortex, including winter storms and severe weather.
Snow and ice are often pressing concerns during these colder months, making awareness of these patterns crucial for residents.
Consequences of a Reversing Polar Vortex

The polar vortex, when it spins backwards, can lead to significant changes in weather and atmospheric conditions. Understanding these effects helps in predicting how such events might influence global weather patterns, especially regarding extreme conditions like cold snaps and storms.
Atmospheric Changes During Reversal
A polar vortex reversal often follows a sudden stratospheric warming. This event temporarily disrupts the cold air normally contained within the vortex. As the stratosphere heats up, it can change the flow of air, pushing the cold air southward.
This shift leads to a phenomenon known as “polar ozone” depletion, which can cause increases in ozone levels at lower altitudes. During this time, atmospheric scientists monitor changes carefully, as elevated ozone levels can impact weather systems. The result can be odd weather patterns that can affect multiple regions globally.
Effects on Weather Patterns Globally
The impacts of a reversing polar vortex are not limited to the Arctic. When cold air moves south, it can trigger freezing temperatures far from its origin. This can lead to severe cold snaps in areas like Canada and parts of the U.S. During these events, temperatures can drop drastically and lead to frozen precipitation.
Additionally, the reversal can influence storms in regions that typically have milder weather. For instance, certain areas could see dramatic shifts, like the return of winter storms despite the season suggesting a different pattern. Depending on the strength of the reversal, it can lead to disruptive weather systems extending across the continent.
Role of Climate Change in Vortex Behavior
Climate change has become a critical factor in how the polar vortex behaves. Warmer global temperatures can influence the frequency and intensity of vortex reversals. This is concerning as it may lead to more extreme weather events in the future.
Researchers are investigating links between increased temperature and patterns like El Niño, which may interact with polar vortex dynamics. As the Arctic continues to warm, it is essential to understand its effects on the ozone hole and how chemical ozone loss could accelerate these changes, causing unpredictable weather impacts worldwide.
Predicting and Responding to Vortex Reversals
Predicting a polar vortex reversal is complex.
Meteorologists rely on advanced models and real-time data to forecast these events.
As the stratosphere warms, the planetary waves that guide air movement can provide insight into pending changes.
Being prepared for the consequences of a reversal is crucial.
Governments and local authorities need to establish protocols to handle unexpected weather developments.
Community preparedness for sudden cold weather is essential, particularly in regions where freezing conditions can disrupt daily life.
For further insights on weather patterns, one might explore resources discussing wind and its role in atmosphere dynamics.
