Nor’easters are powerful storms that primarily impact the East Coast, especially regions like New England. They are known for bringing heavy snow, strong winds, and significant coastal flooding.
While there is no widely recognized scale for measuring the intensity of a nor’easter, the Dolan-Davis scale provides a classification based on wave height and storm conditions.
Meteorologists often analyze the effects these storms have on local weather patterns, making it crucial to understand their impact.
The Dolan-Davis scale, developed using extensive data on past nor’easters, categorizes storms from Class I to Class V, focusing on their oceanic features. This classification helps in predicting the storm’s potential impact on communities.
For those living in or visiting the northeast, knowing about nor’easter intensity can be essential for preparedness. Understanding how these storms are rated can provide valuable insight into what to expect during these extreme weather events.
Understanding Nor’easters

Nor’easters are powerful winter storms that can bring heavy snow, strong winds, and coastal flooding to the eastern United States. Their formation involves various atmospheric conditions, which can lead to significant impacts on weather patterns and local communities.
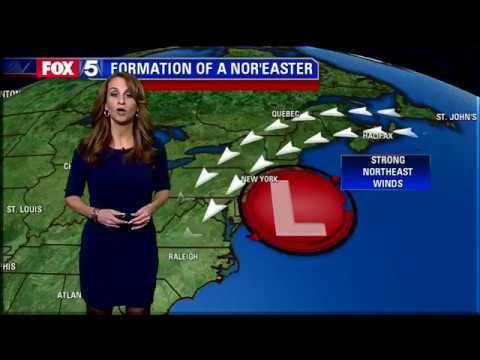
Formation and Characteristics
Nor’easters typically form along the Atlantic coast during the winter months. They arise when cold air from the polar vortex meets warm, moist air from the ocean.
This clash of air masses creates instability, which is crucial for cyclogenesis, the development of low-pressure systems.
As these storm systems develop, they often move northward or northeastward, following the jet stream. The term “nor’easter” comes from the strong northeast winds that accompany these storms.
Bombogenesis, a rapid intensification process, can increase storm intensity, leading to heavy snow and high winds.
Nor’easter Intensity and Impact
The intensity of a nor’easter can vary greatly, but storms often reach peak intensity when winds exceed 40 mph and snowfall rates surpass 2 inches per hour. This can create blizzard conditions, making travel extremely dangerous.
The Regional Snowfall Index (RSI) measures the impact of these storms based on snowfall amounts and wind conditions. Coastal areas are especially vulnerable to flooding due to high winds and rising seas.
The National Weather Service plays a crucial role in issuing alerts about nor’easters, helping communities prepare for heavy snow and potential impacts on daily life.
Understanding the risks associated with nor’easters helps individuals stay safe during these significant winter storms. For more information on snow and ice, as well as wind, readers can explore additional resources.
Measuring the Intensity of Nor’easters
Measuring the intensity of nor’easters is essential to understanding their impact on weather events and snow accumulation in the Northeastern United States. Two key methods for classification are the Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale (NESIS) and the Regional Snowfall Index (RSI). These methods help categorize storms based on their severity and effects.
The Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale (NESIS)
The Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale (NESIS) classifies winter storms based on their impact rather than just snow accumulation. Developed in the early 2000s, NESIS rates storms from Category 1 to Category 5, focusing on factors like snowfall amounts, geographic area affected, and population impact.
- Category 1: Minor impact, light accumulation.
- Category 3: Moderate, widespread impacts.
- Category 5: Extreme, massive disruption.
Major storm events, like the “Superstorm of 1993” and the “North American Blizzard of 1996,” often receive Category 4 or 5 ratings. NESIS is valuable for understanding how snowstorms affect daily life in areas like New England and the Mid-Atlantic regions.
The Regional Snowfall Index (RSI)
The Regional Snowfall Index (RSI) is another tool for analyzing nor’easters, focusing on total snow accumulation over time.
It was designed to create a standardized way to evaluate the impact of significant snowstorms in the eastern United States.
RSI considers several factors, such as:
- Snowfall depth
- Duration of the storm
- Area impacted
Higher RSI values indicate greater storm impacts, which helps meteorologists assess and compare historical storms.
For instance, the “Blizzard of 1888” holds an impressive record for its high RSI score, showing just how severe winter storms can be.
This tool offers critical insights into storm tracks and return periods in affected areas.
More detailed analyses of these storms can be found through regional articles.
