Among the many awe-inspiring natural phenomena on our planet, the Kilauea Volcano in Hawaii stands out as the most active volcano in the world.
Its frequent eruptions and unique characteristics make it a focal point for volcanologists and adventure seekers alike. Kilauea not only features a lava flow that has been highly active for decades, but it also sends ash plumes high into the atmosphere, impacting air travel and local weather patterns.
Kilauea is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area known for its seismic activity and numerous active volcanoes. The continuous eruptions from Kilauea create a dynamic landscape that is constantly changing.
This volcanic activity provides valuable insights into earth processes and the behavior of magma as it moves beneath the Earth’s crust.
As Kilauea continues to evolve, the fascination with its eruptions grows. Researchers study its patterns to better understand volcanic activity, which can be crucial for predicting future eruptions and their potential impact on nearby communities.
Understanding the Most Active Volcanoes
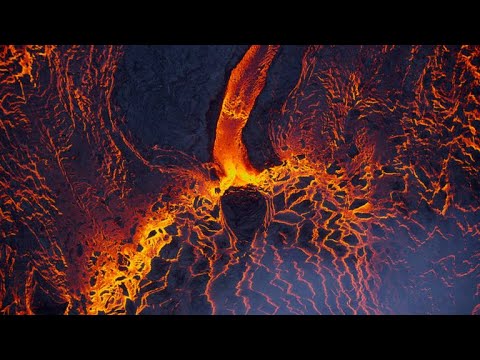
Active volcanoes play a crucial role in Earth’s geology and can greatly affect local ecosystems and communities. This section explores their geography, key characteristics, and current monitoring efforts to provide a clearer picture of these powerful natural phenomena.
Geography and Distribution
Most active volcanoes are found along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a major area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur.
Countries like Indonesia, known for its Lava flows and Strombolian explosions, are home to multiple active volcanic sites. Notable examples include Mount Merapi, a highly active volcano in Java, and Mount Sinabung.
Iceland also has significant volcanic activity, marked by Eyjafjallajökull, which famously disrupted air travel in 2010. Other active regions include the Canary Islands and the Reykjanes Peninsula, both of which are part of ongoing volcanic research.
Key Characteristics
Volcanoes exhibit various characteristics that define their activity. For example, lava lakes are a striking feature found in several volcanos, where molten lava accumulates in a crater.
The most active volcanoes erupt frequently, displaying a mix of explosive and effusive eruptions. Eruptions create volcanic ash that can be hazardous to air travel and human health.
They can also be classified into different types based on their eruption style. For instance, Strombolian eruptions produce periodic bursts of lava and gas, while others might yield quieter lava flows.
Volcanologists study these features to understand and predict volcanic activity, focusing heavily on areas with a history of eruptions.
Current Monitoring and Research
Monitoring the world’s most active volcanoes is vital for public safety and scientific understanding. Researchers use a variety of tools, including seismology, to detect tremors that may indicate an impending eruption.
Satellite imagery is also essential for tracking changes in volcanic terrain and heat emissions. In Indonesia and Iceland, government agencies work alongside international organizations to keep communities informed of volcanic activity.
This includes tracking ash dispersal to manage flight paths and safeguard air travel. Continued research at active sites helps scientists better predict eruptions, which can save lives and reduce property damage.
Efforts include studying the links between volcanic activity and climate patterns, adding another layer of importance to ongoing monitoring initiatives.
Safety, Preparedness, and Impact

Understanding safety measures and preparedness can help reduce the risks associated with volcanic eruptions. This section outlines key aspects of evacuation plans and safety protocols, as well as the economic and environmental consequences of eruptions.
Evacuation Plans and Safety Measures
Evacuating an area near a volcano is critical when warnings indicate imminent danger. Authorities develop detailed evacuation plans based on the type of eruption and population density.
These plans include designated safe zones, transportation options, and communication systems. Residents should stay informed about the risks of ash plumes and lava flow.
It is vital to prepare an emergency kit with necessary supplies like food, water, and medications. Community education on safety protocols, like recognizing volcanic signs and evacuation routes, is essential.
Engaging with local emergency services can ensure that families know the safest evacuation routes and procedures if dangerous volcanoes show signs of activity.
Economic and Environmental Consequences
The economic impact of volcanic eruptions can be severe.
Damage from volcanic ash can disrupt local businesses, impact agriculture, and even affect global supply chains.
The financial losses can amount to millions, affecting jobs and local economies.
Environmentally, eruptions contribute to climate change by releasing ash and gases into the atmosphere.
This can alter weather patterns and affect air quality, leading to public health issues.
The eruption of a volcano can also devastate local ecosystems, affecting wildlife and natural resources.
Understanding these impacts is crucial for preparing effective response strategies during volcanic events.

