Rain is more than just water falling from the sky; it can also be a source of energy. Raindrops possess kinetic energy as they fall, and researchers are exploring ways to harvest this energy for electric power generation.
This intriguing concept could revolutionize how we think about energy sources and sustainability.
By capturing the energy from falling raindrops, we could harness both kinetic energy from their movement and potential energy from their impact. Technologies are being developed to convert this natural energy into usable power, paving the way for innovative solutions in energy harvesting.
The potential applications of this technology could make a significant impact on our approach to renewable resources.
Explore more about water’s role in energy by checking articles on water.
As the quest for green energy continues, understanding how rain can contribute to electric power opens up new possibilities. This efficient approach to capturing energy is not just a theory; it is becoming a reality as research advances.
The potential of rain as an energy source deserves attention, especially as the world shifts toward more sustainable practices.
Physics of Rain Energy
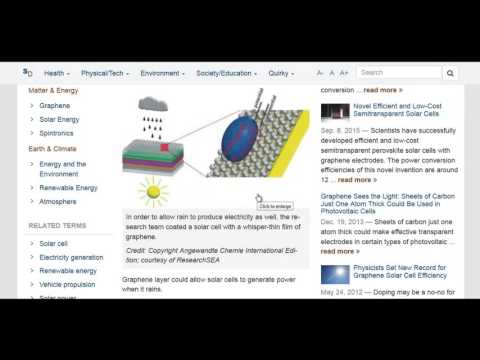
Rain carries significant energy that can be harnessed in various ways. This energy primarily consists of kinetic energy from falling raindrops and the potential energy associated with their height.
Additionally, advancements in technology have opened avenues for converting this energy into electricity.
Kinetic Energy of Falling Rain
As raindrops fall, they gain kinetic energy due to gravity. This energy can be calculated using the formula:
Kinetic Energy (KE) = 1/2 mv²
Where m is the mass and v is the velocity of the raindrop.
Larger and faster raindrops contribute more energy. For instance, a single raindrop can have enough kinetic energy to power small devices when collected in larger quantities.
Falling Distance is also crucial since drops falling from greater heights possess more gravitational potential energy that transforms into kinetic energy as they descend. Understanding this relationship is vital for effective energy conversion strategies in rain energy systems.
Electrical Energy Conversion
The conversion of raindrop energy into electricity mainly relies on piezoelectric materials. These materials generate an electric charge when subjected to mechanical stress, such as the impact of falling rain.
When raindrops strike a piezoelectric surface, they induce a surface charge, leading to electricity generation.
Moreover, researchers have explored various methods to improve the efficiency of this conversion.
For example, harnessing energy from multiple drops simultaneously can enhance electricity output.
Such innovations can contribute to sustainable energy solutions, especially in areas with frequent rainfall.
Technologies that convert kinetic energy into electric power will play a significant role in future energy systems, making rain a valuable energy source.
For more insights into this topic, visit articles on atmospheric phenomena.
Technological Applications and Implications

Recent advances show that rain can be a viable source of energy, leading to exciting new technologies. These innovations might significantly impact renewable energy systems, influencing power generation and sustainability. Understanding these developments is crucial.
Rain Energy Harvesting Technologies
Rain energy harvesting technologies utilize unique methods to capture energy from falling droplets.
One common approach involves the use of piezoelectric materials, which can generate electricity when compressed. These materials can be placed in areas where rainfall is abundant, transforming mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Another promising method includes droplet-based electricity generators. These devices convert the kinetic energy of rain into usable power. As raindrops fall, they create motion that can be harvested through specially designed surfaces.
Recent innovations in nanogenerators also show potential. These tiny devices can collect energy from small environmental movements, including raindrops. The energy accumulated can feed into the local energy grid or be stored for later use, improving overall energy efficiency.
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
Integrating rain energy harvesting with other renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, holds great promise.
For instance, a system that captures energy from rain can complement hydroelectric power and enhance the overall energy output.
This integration may lead to more consistent energy generation, especially in regions with variable weather patterns.
Additionally, rain energy can help stabilize power supply during periods of low solar or wind energy production.
Using multiple renewable sources can increase reliability and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
This innovative approach underscores the need for a diversified energy portfolio, reducing risks associated with energy shortages.
The combined use of renewable energy sources can create a more resilient energy infrastructure, capable of adapting to changing conditions and maximizing energy generation efficiency.
