Floods can devastate communities, turning normal landscapes into scenes of chaos and destruction.
Human activities significantly contribute to the risk of flooding by altering natural environments and drainage systems.
Factors such as urban development, deforestation, and climate change play crucial roles in increasing flood occurrences and severity.
As cities expand, natural waterways are often blocked or redirected, preventing water from flowing freely. This disruption can lead to higher flood risks, especially during heavy rainfall.
Furthermore, climate change intensifies weather patterns, resulting in more extreme storms and heavy downpours that overwhelm existing infrastructure.
Understanding the human causes of floods is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
By recognizing how actions like construction, land use changes, and pollution affect flood risks, communities can take proactive steps to protect themselves against future natural disasters.
Human Contributions to Flood Risks

Human activities play a significant role in increasing the risk of floods. Several factors, such as urban development, changes in land use, and climate change, contribute to this problem.
Understanding these aspects can help in finding ways to mitigate flood risks.
Urban Development and Impermeable Surfaces
Urban areas often feature surfaces that do not absorb water, like asphalt and concrete. These impermeable surfaces prevent water from soaking into the ground.
When it rains heavily, water cannot penetrate the soil and instead runs off into streets and gutters.
This increased runoff can overwhelm local drainage systems and lead to flash floods. Many cities have seen rising flood events as they expand.
Poorly designed or maintained sewer systems can fail, causing additional flooding. Urban development often occurs in floodplains, which are naturally prone to flooding. This development further increases risks to nearby communities.
Land Use and Environmental Changes
Human land use, such as agriculture and deforestation, greatly impacts water management. Deforestation removes trees that help absorb water, while agricultural practices often disturb soil.
These changes can increase erosion and reduce the land’s natural ability to hold water.
Wetlands, which act as natural sponges, are frequently drained for development. This loss reduces the overall capacity of the landscape to manage excess water.
More runoff enters rivers, causing river discharge to rise quickly. When heavy rainfall occurs, water may spill over riverbanks, leading to coastal flooding and river flooding in populated areas.
Climate Change Effects
Climate change is causing more extreme weather. This includes heavy rain and atmospheric rivers, which can lead to sudden and intense flooding.
Rising temperatures increase the likelihood of extreme rainfall events.
Moreover, greenhouse gas emissions contribute to global warming, which causes sea level rise. Coastal flooding is becoming more common as rising seas threaten low-lying areas.
Increased rainfall can also overwhelm existing drainage systems that were not designed for such extreme weather events. As climate change progresses, the frequency and severity of floods are likely to increase, posing more risks to communities.
Impact of Flood Events
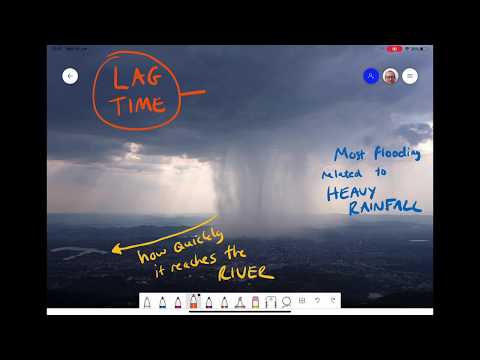
Flood events can significantly disrupt both economies and ecosystems. They lead to destruction of infrastructure and create various health risks due to contamination and diseases. The effects span far beyond immediate damage, impacting communities for years to come.
Economic and Infrastructure Damage
Flooding can incur massive economic losses for affected regions. Businesses may face shutdowns, and local economies can struggle to recover.
For instance, in flood-prone areas, damage to roads and bridges requires extensive reconstruction.
The United Nations has reported that flooding can result in billions in infrastructural costs. Property damage often leads to increased flood insurance claims, further straining financial resources.
The need for improved flood control systems, such as levees and retention basins, becomes crucial to mitigate future risks.
Governments also need to allocate funds for rebuilding communities, which can divert money from other essential services. Long-term economic implications include increased taxes and property values decreasing due to perceived flood risks.
Environmental and Health Concerns
Floods can also cause severe environmental issues. They lead to erosion and disturb wetlands, which are vital for natural water management and biodiversity.
Contamination of water sources often occurs when sewage systems overflow, resulting in hazardous waterborne diseases.
After flooding, areas may see a rise in mosquito populations, increasing the risk of diseases such as West Nile virus. Restoration of natural habitats is critical for controlling breeding and dispersal of disease vectors.
Moreover, climate change exacerbates flooding events, making it necessary for communities to adapt. Protecting ecosystems can help mitigate some flood impacts, ensuring a balance between human needs and environmental health.
The need for community awareness and preparedness becomes paramount in facing these challenges.

