Hydrology plays a vital role in understanding how water interacts with the environment. This field focuses on the movement, distribution, and quality of water, making it crucial for numerous applications.
Hydrology is both a science and an engineering discipline. It involves scientific study and practical application to manage water resources effectively.
In the science of hydrology, researchers analyze data and develop theories about water cycles, climate impacts, and ecosystem health. Meanwhile, engineering applies these scientific principles to design solutions for water management, flood control, and sustainable practices.
This blending of science and engineering helps professionals address challenges related to water, from urban development to conservation efforts.
Readers interested in the interplay between these fields will find that the answers to pressing global challenges often lie at the junction of hydrology and engineering. Understanding this relationship is essential for developing effective responses to issues like water scarcity, pollution, and climate change impacts.
Hydrology as a Science
Hydrology is a pivotal science that focuses on water in various forms and its impact on the Earth’s systems. It studies how water moves, its characteristics, and its role in the environment.
This section explores critical components of hydrology, including the water cycle, groundwater, and surface water dynamics.
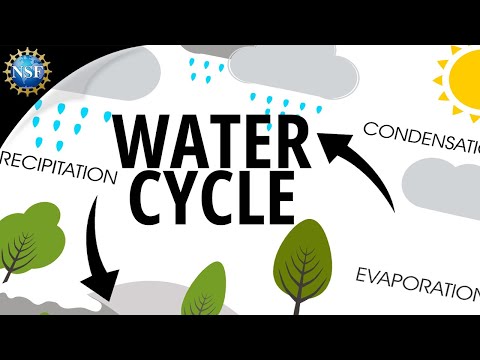
Understanding the Water Cycle
The water cycle explains how water moves through the environment. It involves various processes like precipitation, evaporation, and transpiration.
Precipitation includes forms such as rain and snow, which replenish surface and groundwater. Once water reaches the ground, it either runs off into bodies of water or seeps into the earth. It then evaporates back into the atmosphere or is taken up by plants through transpiration.
This cycle is crucial for maintaining water resources and influencing climate change. Understanding the water cycle helps predict water availability and manage water resources.
Groundwater and Aquifers
Groundwater is stored in aquifers, which are layers of rock and soil that can hold significant amounts of water. They play a critical role in supplying drinking water and irrigation.
The study of groundwater involves hydrogeology, focusing on how water flows through soil and rock formations.
Aquifer health is essential for sustainable water access. Factors like over-extraction can deplete these resources, leading to decreased water availability. Additionally, groundwater often interacts with surface water, impacting streamflow and river flow patterns.
Protecting aquifers is vital for maintaining the balance of water in the environment.
Surface Water Dynamics
Surface water includes rivers, lakes, and streams, all essential components of the hydrologic cycle. The movement of water in these bodies impacts ecosystems, agriculture, and human settlements.
Streamflow describes the flow of water in channels and rivers, affected by precipitation and evaporation rates.
Changes in land use, climate variations, and pollution can significantly alter surface water dynamics. Managing surface water is crucial for flood control, irrigation, and conservation efforts.
The interaction between surface water and groundwater also plays a role in maintaining the overall health of aquatic systems. Strategies must focus on sustainable practices to ensure the continued availability of these vital resources.
For insights into broader aspects of water and its importance, visit Water – ChaseDay.com.
Applications in Engineering Hydrology

Engineering hydrology plays a crucial role in effectively managing water resources and protecting the environment. Its applications span various fields, from resource management to technological innovations that enhance water quality and sustainability.
Management of Water Resources
Efficient management of water resources is essential in areas like irrigation and flood control. Through hydrological modeling, engineers can predict water availability and manage its distribution effectively.
This modeling helps design effective irrigation schemes that optimize water use, ensuring crops receive adequate moisture.
Engineers also use data analysis to determine groundwater levels, assess water supply needs, and address pollution concerns. Techniques such as remote sensing aid in monitoring water bodies, allowing for timely interventions in pollution control.
By managing water resources efficiently, engineers promote sustainability while supporting ecosystems.
Environmental Protection and Sustainability
Hydrology is vital in promoting environmental protection and sustainability. Engineers assess water quality to monitor pollution levels, helping to protect ecosystems and maintain biodiversity.
Innovative solutions in environmental engineering work towards minimizing negative impacts on water bodies.
The design of hydroelectric power plants utilizes hydrological data to ensure efficient energy production while minimizing ecological disruption. This form of renewable energy contributes to reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Furthermore, engineering practices must incorporate sustainable methods to protect habitats and promote biodiversity in nearby ecosystems.
Technological Advances and Data Analysis
Recent technological advances enhance the analysis and management of hydrological data.
The integration of machine learning and statistical methods allows for more accurate predictions related to water flow and quality.
These technologies streamline processes and enhance the decision-making capabilities of water resources engineers.
Innovations such as advanced remote sensing equipment provide real-time data on surface and groundwater conditions.
This information aids in addressing issues like flood control and water supply management.
Accurate data is essential for implementing solutions that ensure efficient use of water resources while safeguarding the environment.
For instance, the monitoring of surface movement helps engineers understand how water interacts with land, informing better infrastructure development.
Through these technological advancements, engineering hydrology continues to evolve, ensuring more effective management of vital water resources.
