Snowfall patterns are changing across the globe, raising questions about their future in a warming world. Recent studies show that overall, snowfall is decreasing due to climate change, with many regions experiencing less precipitation falling as snow.
This trend can have significant effects on winter weather, snow cover, and the ecosystem.
As temperatures rise, the ability of the atmosphere to hold moisture changes, leading to less snowfall in some areas. In fact, nearly 80 percent of measuring stations in the contiguous United States report less precipitation in the form of snow.
The changes in snowfall impact not only winter sports enthusiasts but also water supply, as snowpack plays a vital role in providing freshwater during warmer months.
Understanding these shifts in snowfall is crucial for preparing for the impacts of global warming. By examining the connection between climate and snowfall trends, it becomes clear that monitoring these changes will be essential in addressing future environmental challenges.
Analyzing Snowfall Trends
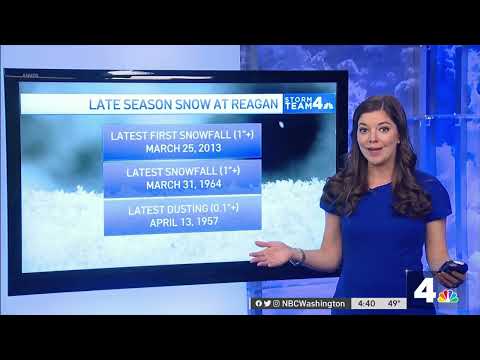
Snowfall trends indicate significant changes in both total snowfall and regional patterns. These shifts are influenced by climate dynamics and have differing impacts across various regions.
Understanding these trends helps to grasp the broader implications of climate change on winter precipitation.
Global Snowfall Observations
Across the globe, snowfall has generally decreased over recent decades. Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows that nearly two-thirds of weather stations report lower snowfall compared to the early 1970s.
Many areas, particularly in the Midwest and parts of Europe, have experienced significant declines. The Global Historical Climatology Network has tracked these changes, emphasizing a reduction in total snowfall.
In some regions, early winter snow is melting faster, impacting ecosystems and water resources. Changing precipitation patterns are largely attributed to global warming, where increased temperatures result in more winter rain instead of snow.
Regional Snowfall Variations
Regional variations illustrate the uneven nature of snowfall trends. The Great Lakes region, for instance, has seen fluctuations in snowfall due to lake-effect snow but still suffers overall declines.
In contrast, parts of Asia have experienced heavier snowfalls in specific areas, yet broad statistics reflect a general downward trend. The National Weather Service provides insights into these regional differences, highlighting that some areas may rise in snowfall due to localized weather phenomena.
This complexity underscores the need to study regional climates in detail, as trends may vary widely even within short distances.
Influences of Climate Dynamics
Several climatic factors drive changes in snowfall. Notably, the jet stream plays a crucial role in shaping winter weather. Variations in temperature can disrupt its usual patterns, leading to altered snowfall distribution.
Additionally, el Niño and la Niña events are known to influence winter precipitation significantly. These phenomena affect global temperatures and can lead to dramatic changes in snowfall in susceptible areas, including parts of Asia and Europe.
As winter temperatures continue to rise, the balance between rain and snow shifts, further complicating snowfall dynamics.
Predictive Snowfall Models
Predictive models are essential for understanding potential future snowfall trends. These models utilize historical data and climate projections to forecast changes in total snowfall.
By analyzing trends from weather stations, researchers can estimate how global warming will affect snowfall in upcoming decades. Certain areas may see continued declines while other locations, influenced by specific factors, may experience increases.
Accurate forecasting is vital for resource management, sporting activities, and preparing for climate-related challenges. Enhanced models can incorporate changing weather patterns, providing clearer insights into future snowfall trends. For specific data on weather and snow dynamics, exploring articles on snow and ice can offer further information.
Impacts on Environment and Society

The changes in snowfall have significant effects on various aspects of both the environment and society. Key areas include water resources, agriculture, winter sports, and the economy. Each is impacted by shifts in snow dynamics and climate patterns, which can reshape how communities function.
Water Resources and Supply
Snow plays a critical role in replenishing water supplies through snowmelt. In places like the Sierra Nevada, melting snow provides water for rivers and reservoirs, essential for drinking and irrigation.
Decreased snowfall can lead to reduced snowpack, impacting the Colorado River and other river basins. This can cause problems like drought and diminished water supplies during warmer months.
As favorably warm winters continue, evaporation rates from reservoirs increase, further straining available water. This has led to increased competition for limited resources.
Agriculture and Food Security
Farmers rely on snowmelt as a water source for crops. In regions with less snow, agriculture is threatened, impacting food security.
The Northern Great Plains are seeing changes in crop yields due to shifting snowfall patterns. If snow cover decreases, vital moisture levels in the soil can drop, leading to drought conditions that affect crop growth.
This can result in higher food prices and reduced availability in markets, making it harder for many to access fresh produce.
Winter Recreation and Sports
For winter sports enthusiasts, changing snowfall patterns can disrupt traditional activities such as skiing and snowboarding. Resorts depend on consistent snowfall to maintain operations.
A decline in winter snow can lead to shorter seasons, hindering business and limiting recreational options. Areas that see decreased snowfall may experience economic challenges as tourists put less money into local economies.
Conversely, some locations are beginning to see an increase in snowstorms, changing typical winter recreation dynamics, which can either help or hurt certain regions in the winter sports industry.
Economic Considerations
The economic impact of changing snowfall is broad, affecting everything from local businesses to tourism.
Increased average winter temperatures can lead to fewer visitors to winter resorts, affecting jobs and income in those areas. On the other hand, areas that benefit from increased snowfall, such as sites with lake effect snow, may experience a boost in tourism.
The economic implications are complex, as communities must adapt to the shifting patterns of snowfall and address the effects of wildfires and other climate-related disruptions.
Adjustments and investments in infrastructure may be necessary to maintain economic stability in an evolving climate.
Evolving snow dynamics reveal the interconnected challenges that climate change presents for communities and ecosystems, influencing daily life and long-term sustainability.
