Rain is a vital part of our planet’s ecosystem and plays a crucial role in the water cycle. Rain occurs when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into droplets that become heavy enough to fall to the ground.
This process is influenced by various factors, including temperature, humidity, and air pressure, all of which are interconnected in the climate system.
As water evaporates from bodies of water, it rises into the atmosphere where it cools and forms clouds. When these clouds gather enough water droplets, they can produce precipitation in the form of rain, snow, or other types.
Understanding the mechanics of rain not only helps in weather forecasting but also in appreciating the complexities of our natural world.
To learn more about how atmospheric conditions contribute to various weather patterns, explore articles on atmospheric phenomena.
Knowing what creates rain is essential for agriculture, water resources management, and even daily life planning. People around the world depend on rainfall for drinking water, crop irrigation, and much more.
By exploring the science behind rain, readers can better appreciate its importance and the delicate balance of the environment.
The Science of Rain Formation
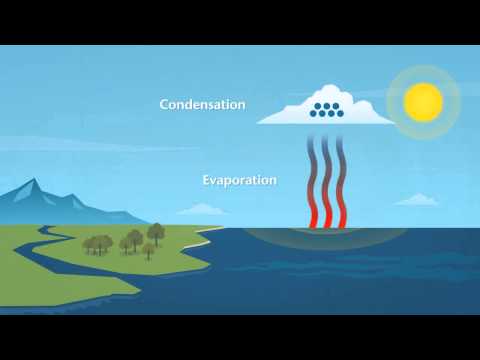
Rain formation is a complex process influenced by several atmospheric conditions. Understanding how water vapor moves and condenses into droplets helps explain how rain falls from the sky.
Water Cycle and Atmospheric Conditions
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
It begins with the evaporation of water from oceans, rivers, and lakes, where sunlight heats the water, turning it into water vapor. This vapor rises into the atmosphere, where temperatures drop.
Humidity plays a critical role during this phase. When the air becomes saturated with water vapor, it cannot hold any more moisture.
As air cools, the water vapor condenses into tiny droplets. These droplets form clouds, often aided by dust particles that serve as nucleation sites. This process ensures that clouds can become dense enough for rainfall to occur.
Cloud Formation and Rainfall Mechanisms
Cloud formation starts when warmer air rises and cools, leading to condensation. As the temperature changes, water vapor turns back into liquid, forming small droplets that cluster together.
When these droplets collide and merge, they create larger droplets, eventually falling as raindrops when heavy enough.
Transpiration from plants also contributes to the moisture in the atmosphere. Plants release water vapor, adding to the humidity.
Techniques like cloud seeding may enhance precipitation by introducing additional particles into clouds, encouraging more condensation and larger droplets. This is particularly useful in managing water resources, especially in arid regions.
Understanding these processes, including the nuances of temperature and surface movement, is crucial for predicting rainfall patterns and weather phenomena.
Rain’s Effects on the Environment and Society

Rain plays a critical role in shaping ecosystems and affecting daily life. Its impact can be positive, such as supporting agriculture and filling rivers, or negative, leading to flooding and environmental challenges.
Impact on Ecosystems and Climate
Rainfall is essential for maintaining ecosystems. It provides fresh water to rivers, streams, and aquifers. This water is crucial for plants, animals, and humans alike.
In areas with abundant rainfall, such as rainforests, diverse species thrive, creating complex habitats.
The amount of rain also affects climate. Regions with heavy rainfall tend to be cooler compared to arid areas, which can suffer from drought.
Acid rain poses another threat, impacting soil and water quality, which can harm both wildlife and agriculture. Precipitation patterns influenced by factors like topography and temperature contribute to the health of these ecosystems over time.
Societal and Environmental Challenges
Rain impacts society significantly, especially in urban areas.
Heavy rainfall can lead to severe flooding, causing property damage and disrupting lives. This is particularly concerning in cities with poor drainage systems.
Drought, often caused by inconsistent rainfall, poses challenges for agriculture.
Farmers depend on reliable moisture for crops, and insufficient rain can lead to food shortages.
Runoff from rain can carry pollutants into water systems, affecting both freshwater availability and quality. It raises concerns for public health, highlighting the need for better management of water resources.

