Rain clouds play a crucial role in the Earth’s water cycle and weather patterns. The scientific term for rain clouds is “nimbus” clouds, which encompass both nimbostratus and cumulonimbus varieties.
These clouds form in the atmosphere when water vapor condenses into water droplets, resulting in precipitation.
Nimbus clouds can appear in various shapes and sizes. Nimbostratus clouds are thick, gray layers that cover the sky and lead to steady rain. In contrast, cumulonimbus clouds are towering and associated with thunderstorms, often bringing heavy rain, hail, and lightning.
Understanding the formation of these clouds can help predict weather changes and prepare for precipitation events.
For those intrigued by atmospheric phenomena, exploring how these rain clouds develop reveals much about our environment and its weather patterns. Keeping an eye on clouds can lead to a deeper appreciation of the science behind weather changes.
Fascinating insights can be found in studies regarding various cloud types and their roles in weather systems.
Cloud Formation and Types

Cloud formation involves the processes that lead to the development of various types of clouds in the atmosphere. Different cloud types contribute to weather patterns and precipitation, making their study essential for understanding meteorological phenomena.
The Science Behind Cloud Formation
Clouds form through a process driven by water vapor in the air. When warm air rises, it cools due to lower pressure at higher altitudes. This cooling process causes water vapor to lose energy, leading to condensation.
Tiny water droplets or ice crystals form around small particles called condensation nuclei, which can be dust or salt.
Humidity also plays a crucial role; as the moisture level in the air increases, the air can hold less water vapor when it cools, leading to cloud formation.
As clouds develop, they can transform into various types, including cumulus, stratus, and cirrus, each characterized by distinct shapes and altitudes.
Classification of Clouds
Clouds are classified into different types based on their shape, altitude, and the weather they produce. The main classifications include:
- Low-level clouds (up to 2,000 meters): Stratus and stratocumulus are common in this group. They often bring light rain and overcast skies.
- Mid-level clouds (2,000 to 6,000 meters): Altostratus and altocumulus can be found here, sometimes indicating upcoming precipitation.
- High-level clouds (above 6,000 meters): Cirrus clouds are thin and wispy, typically signaling fair weather.
The most significant rain clouds are nimbostratus and cumulonimbus. Nimbostratus clouds produce steady rain over large areas. On the other hand, cumulus congestus and cumulonimbus clouds indicate unstable weather and can lead to thunderstorms, showcasing the diverse roles clouds play in meteorology.
Precipitation and Weather Phenomena
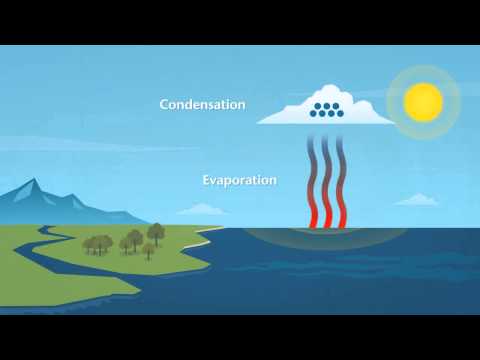
Rain clouds play a vital role in weather phenomena and precipitation. Understanding different types of clouds helps explain how various weather patterns develop and affect daily life.
Rain Clouds and Precipitation
Rain clouds, primarily nimbostratus and cumulonimbus, are essential for producing precipitation. Nimbostratus clouds bring steady rain, whereas cumulonimbus clouds can generate heavy rain and thunderstorms.
These clouds form when moisture in the air rises, cools, and condenses into droplets.
Different types of precipitation can occur, including rain, snow, and hail. Each type is influenced by the temperature and altitude of the cloud. For example, snow forms when temperatures are below freezing, while rain occurs when conditions are warmer.
Understanding these processes helps predict weather events more precisely, such as the likelihood of thunderstorms or snow.
Severe Weather and Clouds
Severe weather can arise from various cloud types, particularly cumulonimbus. These towering clouds can produce dangerous conditions like lightning, thunder, and even tornadoes.
Thunderheads are a common sight during thunderstorms, showcasing powerful updrafts within. Additionally, storm clouds can lead to supercell storms that are capable of producing large hail and intense winds.
Fog can also contribute to reduced visibility during certain weather patterns. Awareness of these phenomena is crucial for forecasting severe weather, allowing people to take precautions.
For more details on specific types of precipitation and their effects, visit articles on snow and ice and electrical storms. Understanding these aspects can enhance everyone’s knowledge of weather systems and their impact on the environment.
