Floods are one of the most devastating natural disasters, impacting communities worldwide.
The major cause of floods is an excessive amount of rainfall over a short period, which can overwhelm rivers and drainage systems. Climate change has made these intense rainfall events more frequent, contributing to the growing risk of severe flooding.
Moreover, other factors such as melting snow, rapid urbanization, and poor land management practices also play significant roles in flood occurrences.
As cities expand, natural drainage is disrupted, making them more vulnerable to flooding. Understanding these causes can help communities better prepare for and mitigate the impacts of future flood events.
Across the globe, the need for effective flood prevention strategies is increasingly urgent. By recognizing the primary triggers of floods, individuals and governments alike can take action to safeguard their environments and reduce the risks involved.
Natural and Environmental Causes of Floods

Floods can be triggered by various natural events. Key factors include meteorological conditions like heavy rainfall and weather systems, as well as geophysical events. Understanding these causes helps in predicting and managing flood risks.
Meteorological Factors
Meteorological conditions play a significant role in flooding.
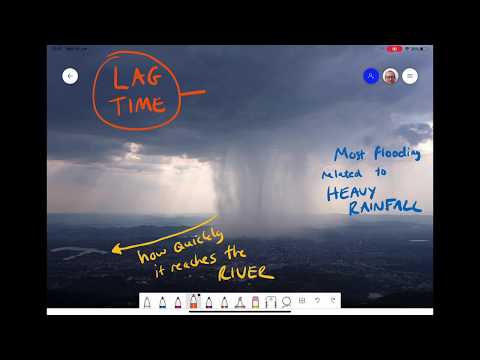
Heavy rainfall, often associated with thunderstorms, can lead to flash floods. These occur when rain falls rapidly, overwhelming drainage systems.
Hurricanes can also cause severe flooding through intense rainfall and storm surges, impacting coastal regions.
Atmospheric rivers are another factor, bringing moist air that can lead to prolonged rain and flooding. In regions with snow, rapid snowmelt during warm weather can also contribute to river flooding. These events combine to create situations where the land cannot absorb or drain the water quickly enough, resulting in extensive flooding.
Geophysical Factors
Geophysical factors include land and earth movements that can cause flooding.
Tsunamis, triggered by underwater earthquakes or landslides, can lead to immediate and violent coastal flooding.
Additionally, river flooding can occur when riverbanks overflow due to excessive rain or ice melt. Floodplains, areas adjacent to rivers, are particularly vulnerable as they act as natural flood reservoirs. Deforestation and urban development can also exacerbate flooding by reducing the land’s natural ability to absorb water, increasing runoff.
Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective flood prevention and response strategies. For more insights into the science behind atmospheric events, explore atmospheric phenomena.
Human Factors and Flood Risk Management
Human actions significantly influence flood risk and management. Urban development and the design of infrastructure play crucial roles in how communities experience and respond to flooding events. Effective planning and mitigation strategies are vital for minimizing flood damage and protecting lives.
Urbanization and Infrastructure
Urbanization impacts flood risk by increasing impervious surfaces, which prevent water absorption.
Cities often replace fields and forests with buildings and roads. This change leads to more runoff during heavy rains, overwhelming drainage systems.
Many urban areas depend on dams and levees to manage water flow. While these structures can reduce flooding, they are not fail-proof. Poor maintenance or design flaws can lead to severe flooding. Flood maps are essential to identify high-risk zones, helping to guide development and emergency responses.
Prevention and Mitigation
Effective flood risk management involves prevention and mitigation strategies.
These include improving drainage systems and enhancing floodplain management.
Communities often invest in retrofitting infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events.
Flood insurance provides financial protection for property owners, helping them recover after floods.
The National Flood Insurance Program encourages communities to adopt better flood management practices.
Emergency response plans are also crucial.
They ensure rapid action during flooding, reducing damage and saving lives.
A comprehensive approach to flood risk management involves a mix of engineering, community planning, and strong policies to protect vulnerable areas.
