Flooding is a significant natural disaster that occurs when water overflows onto normally dry land.
In basic science, a flood is defined as an excess of water resulting from various factors such as heavy rainfall, river overflow, or storm surges. These events have been intensified by climate change, leading to more frequent and severe flooding across the globe.
Understanding the meaning of flooding is crucial as it impacts both human life and the environment.
Floods can arise from sudden, intense rainfall or prolonged periods of heavy rain, which overwhelm drainage systems and rivers. Such occurrences can lead to widespread destruction and pose serious risks to infrastructure and safety, as communities struggle to manage the effects of excess water.
To better grasp the different types and causes of flooding, one can explore related atmospheric phenomena.
Knowledge of these systems helps people prepare for and respond to the challenges posed by floods, supporting efforts to reduce damage and protect lives.
Understanding Floods

Floods are significant natural events that can have serious consequences for environments and communities. They result from various factors and can occur in multiple forms. Recognizing their causes, types, and effects is important for preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Causes of Floods
Floods can arise from several factors.
Heavy rainfall is a primary cause, often leading to river floods as water levels exceed normal capacity. Flash floods occur suddenly, often due to intense rainstorms, causing rapid water rise that can overwhelm urban drainage systems.
Other causes include hurricanes, which can bring storm surges that flood coastal areas. Tsunamis can also result in devastating floods during seismic events. Additionally, dam failures can release large volumes of water unexpectedly, creating dangerous conditions downstream. Ice jams can block rivers, causing water to back up and flood adjacent areas.
Land changes like deforestation can contribute to erosion, reducing the land’s ability to absorb rainfall and increasing flood risk.
Types of Floods
Floods are classified into several types based on their causes and characteristics.
River floods occur when rivers overflow their banks, often during prolonged rainfall. Urban flooding happens in cities where drainage systems cannot handle sudden downpours, leading to water pooling on streets.
Coastal flooding often results from storm surges during hurricanes, while flash floods can occur without warning, making them particularly hazardous. The term “100-year flood” represents a statistical measure indicating the likelihood of a flood of that magnitude occurring in any given year.
Wetlands play a critical role in floodplain management by absorbing excess water and reducing flooding impacts. Understanding the types of floods helps in planning effective prevention and response strategies.
Effects on Ecosystems
Floodwaters can have both positive and negative effects on ecosystems.
They help replenish wetlands and provide essential moisture to wildlife habitats. This can promote biodiversity, as flooding can create new areas for plants and animals to thrive.
However, floods can also lead to problems.
High water levels can cause soil erosion and wash away sediments crucial for plant growth. Debris flows, often triggered by heavy rainfall, can devastate landscapes and habitats.
Flooding can also introduce pollutants into ecosystems, harming water quality and aquatic life. The balance of natural environments is delicate, and floods can disrupt food chains and habitat stability. Understanding these effects is vital for managing ecosystems in flood-prone areas.
For more information on water impacts, explore articles about water and surface movement.
Human Interaction and Response
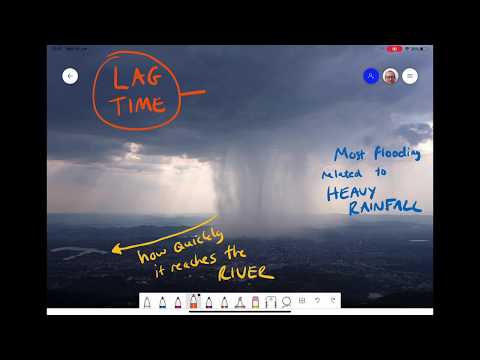
Human interactions shape how communities prepare for and respond to floods. These responses involve risk management, societal effects, and various preventive measures. Understanding these aspects is key to reducing flood damage and improving recovery efforts.
Flood Risk and Management
Flood risk management involves assessing areas prone to floods and developing plans to mitigate harm.
Effective urban planning is crucial, as it ensures that infrastructure can withstand heavy rain and rising water levels. Floodplain management strategies include zoning laws that limit development in high-risk areas.
Emergency services play a vital role in flood risk management.
They implement early warning systems to alert residents about potential flooding. These systems can include text alerts, social media notifications, and sirens. Policies supporting these systems are essential for effective emergency response.
Societal Effects and Recovery
Floods have significant societal effects, impacting communities both physically and economically.
Flood damage can destroy homes and disrupt essential services. Urban areas often face heightened risks due to increased impervious surfaces, which lead to poor drainage and higher floodwaters.
Recovery efforts can be long and complex.
Communities must repair damaged infrastructure and provide support to displaced families. Access to flood insurance is crucial for financial recovery. This can alleviate the economic burden and help residents rebuild their lives.
Preventive Approaches
Preventive approaches focus on minimizing the risk and impact of floods. Levees and embankments serve as barriers to control water flow and protect urban centers.
Thoughtful urban planning ensures that drainage systems are effective and capable of handling heavy rainfall.
Public awareness campaigns educate residents on flood risks and encourage preparedness. Regular flood watch announcements remind communities to stay vigilant during flood seasons.
By understanding their environment and potential hazards, individuals and communities can better protect themselves against natural disasters like floods.
For more on regional flood management and associated topics, check out ChaseDay.com.
