Volcanoes are fascinating and powerful natural wonders that can reshape landscapes and impact lives.
As of now, the most active volcano in the world is Kilauea in Hawaii, which has shown continuous activity. Kilauea’s persistent eruptions not only intrigue scientists and volcanologists but also serve as a reminder of the Earth’s dynamic nature.
Throughout its history, Kilauea has been a significant site for studying volcanic activity.
With its recent eruptions, this volcano has been closely monitored, providing valuable data about the processes that govern volcanic activity and associated earthquakes.
These eruptions contribute to the lush landscapes of Hawaii, highlighting the complex relationship between volcanic activity and the environment.
The excitement surrounding Kilauea also attracts tourists and researchers alike, eager to witness the power of nature.
Staying informed about active volcanoes like Kilauea helps in understanding the potential hazards they pose, while also appreciating their beauty.
For anyone interested in geology, nature, or even adventure, learning about active volcanoes is an engaging journey.
Current Most Active Volcano
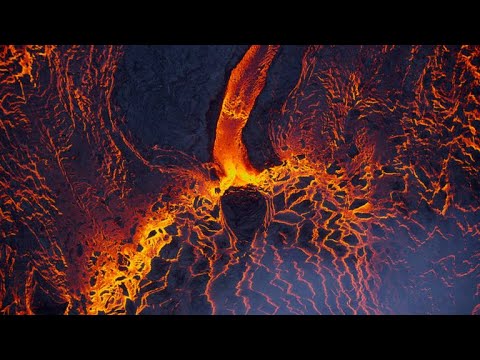
Kilauea in Hawaii is widely recognized as one of the most active volcanoes in the world today. Its frequent eruptions and lava flows draw significant attention from scientists and enthusiasts alike.
This section explores Kilauea’s geological characteristics and its recent activity.
Geological Characteristics
Kilauea is a shield volcano, which means it has broad, gently sloping sides formed by the flow of low-viscosity lava. This type of lava allows for long-distance travel before solidifying.
Kilauea is known for its rift zones, where lava can flow easily, leading to frequent eruptions.
The volcano is primarily composed of basalt rock, which is rich in iron and magnesium. Its summit caldera, measuring about 3 miles wide, contains a lava lake that frequently changes in activity.
Other active volcanoes like Mount Etna in Italy and Stromboli also exhibit unique geological features, but Kilauea’s continuous activity sets it apart.
Recent Activity and Monitoring
Kilauea has been erupting with remarkable frequency. In late 2024, reports noted ongoing lava flows and ash plumes reaching significant heights. Observations indicated that lava fountains were active, with some events producing impressive lava displays.
Monitoring efforts by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) include using seismographs and satellite imagery to track changes in volcanic activity.
This research helps predict future eruptions and assess potential hazards to nearby communities.
Other notable active volcanoes like Fuego in Guatemala and Merapi in Indonesia are also closely monitored for similar reasons.
Global Volcanic Activity

Volcanic activity varies greatly across different regions. Significant eruptions can influence climate and air pollution. Preparedness and response measures help mitigate risks associated with active volcanoes.
By Region
Iceland is known for its active volcanism, particularly on the Reykjanes Peninsula, where eruptions frequently occur. Recent activity has been marked by fissure eruptions and lava flows, drawing attention from scientists worldwide.
In Indonesia, volcanoes such as Manam and Santiaguito pose significant risks. These volcanoes can erupt violently, leading to ash clouds that affect air travel and induce regional health hazards.
Nyiragongo in the Democratic Republic of Congo is another notable volcano, known for its effusive eruptions and lava lakes.
Impact on Climate and Environment
Volcanic eruptions can have a profound impact on climate. For instance, large-scale eruptions can lead to a volcanic winter, resulting from ash and sulfur dioxide particles entering the atmosphere. This can lower global temperatures temporarily, disrupting weather patterns.
Air pollution is another concern. Volcanic ash can contaminate water supplies and damage farmland. It can also cause respiratory problems in nearby populations.
The effects of climate change may exacerbate these impacts, as changes in temperature and precipitation could influence volcanic activity.
Preparedness and Response
Preparedness for volcanic eruptions involves monitoring and alert systems to inform communities of potential threats.
Tools like satellite imagery and ground sensors are vital for tracking volcanic activity.
Local emergency management teams often conduct drills and develop evacuation plans.
Community awareness is essential for minimizing risks when a volcano like Sabancaya erupts.
For sustainable responses, studies on the geological factors of regions with high volcanic activity contribute to better forecasting and preparedness strategies.
Ongoing research into surface movement can enhance understanding of volcanic behavior and improve safety measures.
