Rain is an essential part of Earth’s water cycle and plays a significant role in the environment. The process of rain is called precipitation. This occurs when water vapor in the atmosphere cools and condenses into droplets, which eventually become heavy enough to fall to the ground.
Understanding this process is crucial for grasping how weather systems work and how they impact ecosystems and human activities.
As water evaporates from sources like oceans and rivers, it enters the atmosphere where it contributes to various weather phenomena. The interaction between temperature and humidity leads to the formation of clouds.
When these clouds grow and the accumulated water droplets merge, they release moisture back to the surface in the form of rain.
Exploring the different stages of precipitation can provide insight into both local and global weather patterns, as well as the dynamics of our changing climate.
Meteorologists closely monitor these atmospheric changes since they influence everything from daily weather forecasts to long-term climate predictions. For those interested in atmospheric processes, there is much to learn about how precipitation affects life on Earth and the broader impacts it has on weather systems.
The information can be found in various discussions on atmospheric phenomena.
The Water Cycle and Rain Formation
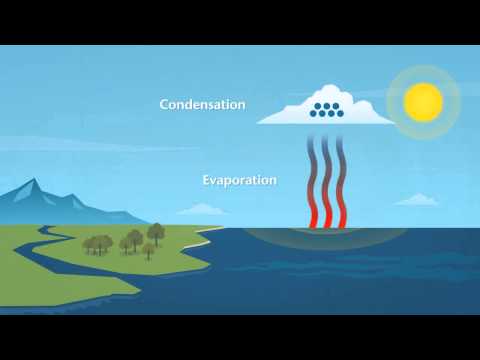
Rain formation is a key part of the water cycle, which connects oceans, rivers, and the atmosphere. Understanding how this process works helps explain why it rains and the types of rainfall experienced in various climates.
Evaporation and Condensation
The journey of rain begins with evaporation. Water from the oceans, lakes, and rivers absorbs heat from the sun and transforms into water vapor. This vapor rises into the atmosphere.
As it ascends, it cools and undergoes a process called condensation.
During condensation, the water vapor turns back into liquid water. Tiny water droplets form and cluster together. This process is essential for cloud formation. The droplets gather in the atmosphere, creating clouds filled with moisture.
The amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere varies. In some locations, it can reach up to 4% of the air. This contributes significantly to the water cycle as water moves from liquid to gas and back again.
For more information on the water cycle, you can explore Water – ChaseDay.com.
Cloud Development and Precipitation
Clouds are made of countless tiny water droplets. When these droplets collide and combine, they grow larger. Eventually, they become heavy enough to fall back to the ground as precipitation, which can be rain, snow, or hail.
The process of forming raindrops involves overcoming air resistance. When droplets become too large, gravity pulls them down, leading to rainfall. The intensity of rainfall can vary based on the size of the droplets and the conditions within the atmosphere.
Different types of clouds indicate varying weather patterns. For example, cumulonimbus clouds are often associated with heavy rainstorms. Understanding cloud development is crucial for predicting weather patterns and the amount of rainfall to expect.
Different Types of Precipitation

Precipitation occurs in various forms, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding these types helps in recognizing their impacts on weather patterns and daily life.
Rain and Drizzle
Rain is the most common type of precipitation, consisting of liquid water droplets that fall when clouds become saturated. Raindrops can vary in size, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 mm in diameter. When conditions are mild, light showers may produce drizzle, which consists of smaller droplets and falls gently.
The formation of rain begins with updrafts in clouds, where moist air cools and condenses to form droplets. These droplets grow larger until gravity pulls them down to the ground.
Occasional heavy rain can lead to flooding, making it essential to monitor local forecasts.
Fog occurs when moisture condenses close to the ground, resulting in low visibility. Rain showers can be brief but intense, affecting outdoor activities. Shifting from light rain to heavier downpours can catch people off guard, making weather awareness critical.
Snow, Sleet, and Other Forms
Snow forms when water vapor in the atmosphere freezes into ice crystals. These crystals cluster and fall as snowflakes, creating a beautiful winter scene.
The size and shape of snowflakes depend on temperature and humidity.
Sleet, or ice pellets, occurs when rain passes through a layer of cold air, freezing before reaching the ground. This form of precipitation can create icy surfaces, leading to hazardous conditions.
Freezing rain, a more dangerous type, occurs when rain falls and freezes on contact with cold surfaces, causing a dangerous layer of ice.
Besides snow and sleet, hail can also be significant. Hailstones form in strong thunderstorms with intense updrafts, resulting in larger pellets of ice.
Understanding these types of precipitation helps prepare for weather conditions, and can be useful in navigating winter weather challenges.
