The study of the atmosphere is known as atmospheric science. This field encompasses various branches, including meteorology, which focuses on weather forecasting, and climatology, which examines long-term climate patterns and changes.
Understanding the atmosphere is crucial as it directly impacts weather conditions, climate change, and the overall health of our planet.
As a discipline, atmospheric science combines elements of physics and chemistry to analyze the Earth’s atmosphere and its phenomena. Meteorologists use this knowledge to make predictions about weather and track severe weather events, which is essential for public safety.
With climate change posing new challenges, the importance of this field has only grown, making it vital for future generations.
In exploring atmospheric science, readers will gain insights into how weather systems work and what drives our planet’s climate patterns. The knowledge gained from studying the atmosphere can enhance our understanding of everything from daily weather forecasts to the long-term impacts of climate change.
Atmospheric Sciences and Their Sub-disciplines
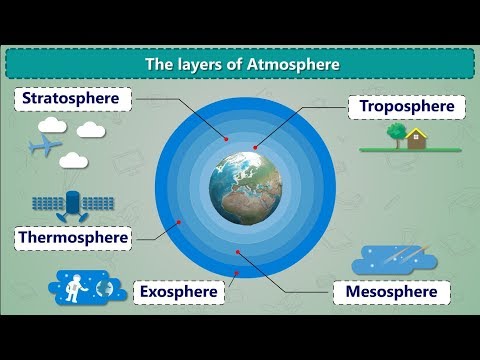
Atmospheric sciences cover various studies related to the Earth’s atmosphere, including its processes and impacts on weather and climate. This field includes several sub-disciplines that focus on specific aspects of atmospheric behavior and characteristics.
Meteorology and Weather Forecasting
Meteorology focuses on the study of the atmosphere, particularly regarding weather systems and forecasting. Meteorologists analyze data from weather stations and utilize tools like radar and weather balloons to gather information.
They monitor factors such as temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure to predict short-term weather conditions.
Advanced technologies enable meteorologists to observe atmospheric phenomena, including storms and precipitation patterns. Accurate weather forecasting is essential for public safety and activities ranging from agriculture to aviation.
The use of remote sensing enhances meteorologists’ ability to understand changing weather conditions and make timely predictions.
Climatology and Climate Change
Climatology examines long-term climate patterns and variability. Climatologists study how factors like greenhouse gases contribute to global warming and ozone depletion.
Understanding these elements is crucial for predicting future climate changes and preparing for their effects.
They analyze historical climate data and current trends to recognize shifts in temperature and precipitation. This knowledge helps governments and organizations develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change and adapt to potential scenarios.
Awareness of climate variability allows societies to manage resources effectively and address environmental challenges.
Atmospheric Physics and Chemistry
Atmospheric physics and chemistry involve studying the physical and chemical properties of the atmosphere. This includes energy transfer processes, cloud physics, and the behavior of gases like ozone.
Atmospheric physicists apply models to understand wave propagation and ionization in the atmosphere.
Chemical models help explain atmospheric reactions, such as those involving pollutants and greenhouse gases. Understanding these interactions is vital for addressing pollution and improving air quality.
By studying atmospheric dynamics, scientists gain insights into weather patterns and their influence on the environment.
Atmospheric Processes and Their Effects on Earth

Atmospheric processes play a crucial role in shaping weather systems and influencing environmental conditions on Earth. They can lead to various weather events and have significant impacts on human health and the environment.
Weather Events and Phenomena
Weather systems, fueled by energy from the sun, create a multitude of atmospheric phenomena. These include thunderstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes, and cyclones.
Thunderstorms can produce heavy rain, hail, or lightning, posing risks to safety and infrastructure. Hurricanes, driven by warm ocean waters, can lead to significant destruction and flooding.
Precipitation, such as rain and snow, is a vital part of the water cycle. It helps replenish groundwater and supports ecosystems.
Additionally, phenomena like El Niño and La Niña (collectively known as ENSO) influence global weather patterns, leading to droughts or excessive rainfall in various regions.
Events like electrical storms can also impact local environments, affecting air quality and creating hazardous conditions for people. For further details, see more about electrical storms.
Environmental and Human Impacts
The effects of atmospheric changes manifest in various forms. Climate change, driven by increased greenhouse gases, has heightened the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events.
Global warming intensifies storms and alters precipitation patterns, affecting agriculture and water supply.
Air quality is also a growing concern, with pollution contributing to respiratory issues and other health problems. Seasonal changes in air pollution can lead to acid rain, damaging ecosystems and infrastructure.
Wildfires, often linked to hot and dry conditions, release pollutants and threaten air quality.
In addition, water vapor from the atmosphere plays a significant role in weather patterns and climate. Its presence affects humidity levels, which can influence human health and comfort.
As weather patterns shift due to climate change, understanding these impacts becomes increasingly important.
