The polar vortex is a significant atmospheric phenomenon that affects weather patterns across the globe.
The last recorded reversal of the polar vortex occurred in early March 2024, a rare event triggered by sudden warming in the stratosphere. This reversal not only changes wind patterns but can also lead to prolonged cold snaps and unusual weather conditions elsewhere.
Climate scientists closely monitor these shifts, as they can have lasting impacts on seasonal weather. The polar vortex typically rotates in a consistent pattern, but when it reverses, it creates chaos in an already volatile atmosphere.
Understanding these changes is crucial for predicting extreme weather events, which can be influenced by the polar vortex’s behavior.
- split text up into at most two sentences per paragraph
- repetitive sentences should be removed
- remove mid-article conclusion paragraphs and sentences
For those interested in the science behind weather systems, the polar vortex serves as a fascinating study of how interconnected our climate is. To explore more about various atmospheric phenomena, visit relevant articles that discuss the intricacies of these events in detail.
Understanding the Polar Vortex Reversal
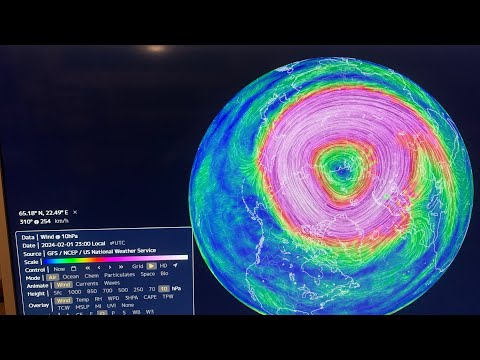
The polar vortex is a large system of winds that circles the polar regions. When it reverses, it can create significant changes in weather patterns across the northern hemisphere.
This section looks at the mechanics behind these reversals, their historical instances, and their connections to sudden stratospheric warming and climate change.
Mechanics of Polar Vortex Reversals
The polar vortex typically spins counterclockwise. A reversal occurs when the winds flip direction due to atmospheric changes.
This flipping usually happens during winter months when disturbances in the atmosphere create waves.
These waves can lead to a sudden surge of warm air into the stratosphere. The increase in temperatures can weaken the polar vortex, causing it to split or reverse. This results in a more erratic jet stream, which can lead to cold weather intruding further south than usual.
When the polar vortex weakens, it may allow cold air to plunge into lower latitudes, which can affect temperatures across the United States and Europe. Such shifts can lead to extreme weather events, including heavy snow and ice storms.
Historical Reversals and Weather Implications
Significant polar vortex reversals have been documented in recent years, notably in 2021 and earlier in 2014. These events can have drastic effects on weather conditions, especially during winter months.
When the polar vortex weakened in early 2021, it resulted in severe cold spells and winter storms across large portions of the Midwest and the southern United States.
Weather patterns can dramatically shift due to these reversals. Instead of warmer conditions that might have been typical for the region, communities may face severe cold. It can lead to dangerous situations, like ice storms and heavy snowfall.
The 2014 reversal, for example, brought frigid air to many parts of North America. This drastic weather change raises concerns about the polar vortex and its influence on climate variability.
Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events
Sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) events are key triggers for polar vortex reversals. An SSW occurs when temperatures in the stratosphere rise rapidly, often by more than 25 degrees Celsius.
This warming can interrupt the normal circulation of winds, resulting in a breakdown of the polar vortex.
These events usually happen in January or February. They can lead to a weakened polar vortex, promoting shifts in the jet stream that contribute to extreme winter weather.
SSW not only affects temperature but also can influence ozone levels in the stratosphere. Ozone spikes can occur during these warming events. This increase can affect health and the environment, showing the far-reaching implications of polar vortex reversals.
The Impact of Climate Change on Polar Vortex Dynamics
The ongoing impacts of climate change are influencing the behavior of the polar vortex. As the climate warms, shifts in temperature and pressure patterns can alter its stability.
Some research suggests that a warming planet may make the polar vortex weaker, increasing the chances of reversal. If this trend continues, it could lead to more severe winter weather events, affecting ecosystems and human activities.
These changes also mean that the interactions between the polar vortex and other atmospheric systems like the jet stream may become more complex. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting future weather patterns and preparing for extreme weather challenges, including heavy snow and ice conditions.
Influence of Global Weather Patterns

The polar vortex significantly impacts global weather patterns, particularly through its interactions with phenomena like El Niño and La Niña. These interactions can influence the movement of Arctic air, which leads to notable shifts in regional weather systems.
Monitoring these patterns helps in understanding how sudden stratospheric warming events affect weather across the Northern Hemisphere.
The Relationship Between El Niño/La Niña Cycles and the Polar Vortex
El Niño and La Niña are part of a broader climate pattern known as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO). During an El Niño phase, warmer ocean temperatures can lead to a stronger polar vortex. This, in turn, often pushes the polar jet stream to more stable positions.
Conversely, La Niña can weaken the polar vortex, allowing frigid Arctic air to spill southward, resulting in cold snaps across North America and parts of Europe. Understanding these cycles is essential, as they dictate shifts in weather, making temperature variations across the globe potentially extreme.
The Effect of Arctic Air on Regional Weather Systems
When the polar vortex weakens, Arctic air can move further south, leading to severe cold outbreaks. This shift impacts various regions, causing intense winter storms and unusual temperature drops.
For instance, during strong disruptions of the polar vortex, the United States may experience prolonged periods of extreme cold. Meteorologists track these influences by observing changes in geopotential height and ozone levels in the stratosphere. Such statistics help predict how cold Arctic air may affect areas not typically influenced by such frigid conditions.
Predictive Weather Modeling by NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) plays a crucial role in forecasting winter weather through advanced modeling techniques.
NOAA utilizes data from satellite imaging and in situ measurements to monitor the polar vortex’s strength and movement.
These models incorporate factors like sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) events, which occur when stratospheric winds shift dramatically.
By analyzing planetary waves, NOAA can provide timely warnings for significant weather changes, aiding in preparation for possible disruptive events like snowstorms.
This robust approach allows for an insightful examination of how the polar vortex shapes weather, benefiting both meteorologists and the general public.
